Imagine you’re baking a cake, and you have a recipe written down on a piece of paper. This recipe contains all the steps you need to follow to bake the cake, from mixing the ingredients to putting it in the oven. A stored procedure in SQL is like that recipe — it’s a set of instructions stored in the database that you can execute whenever you need to perform a specific task or set of tasks.

Example:
Let’s say you want to create a stored procedure for retrieving information about students from a database. The stored procedure will accept the student’s ID as input and return their name and grade.
Here’s how you can create this stored procedure:
CREATE PROCEDURE GetStudentInfo @StudentID INT AS
BEGIN
SELECT Name, Grade FROM Students WHERE StudentID = @StudentID;
END;
Explanation:
CREATE PROCEDURE: This is the SQL statement used to create a new stored procedure.GetStudentInfo: This is the name of the stored procedure.@StudentID INT: This is the input parameter of the stored procedure, specifying the data type (INT) and name (@StudentID) of the parameter.AS: This keyword indicates the beginning of the stored procedure’s body.SELECT Name, Grade FROM Students WHERE StudentID = @StudentID;: This is the SQL query inside the stored procedure. It selects the name and grade of the student with the specified StudentID.
Once you’ve created the stored procedure, you can execute it whenever you need to retrieve information about a student by calling its name and passing the student’s ID as an argument:
EXEC GetStudentInfo @StudentID = 123;
This will execute the stored procedure GetStudentInfo with the student ID 123 as input, and it will return the name and grade of the student with that ID.
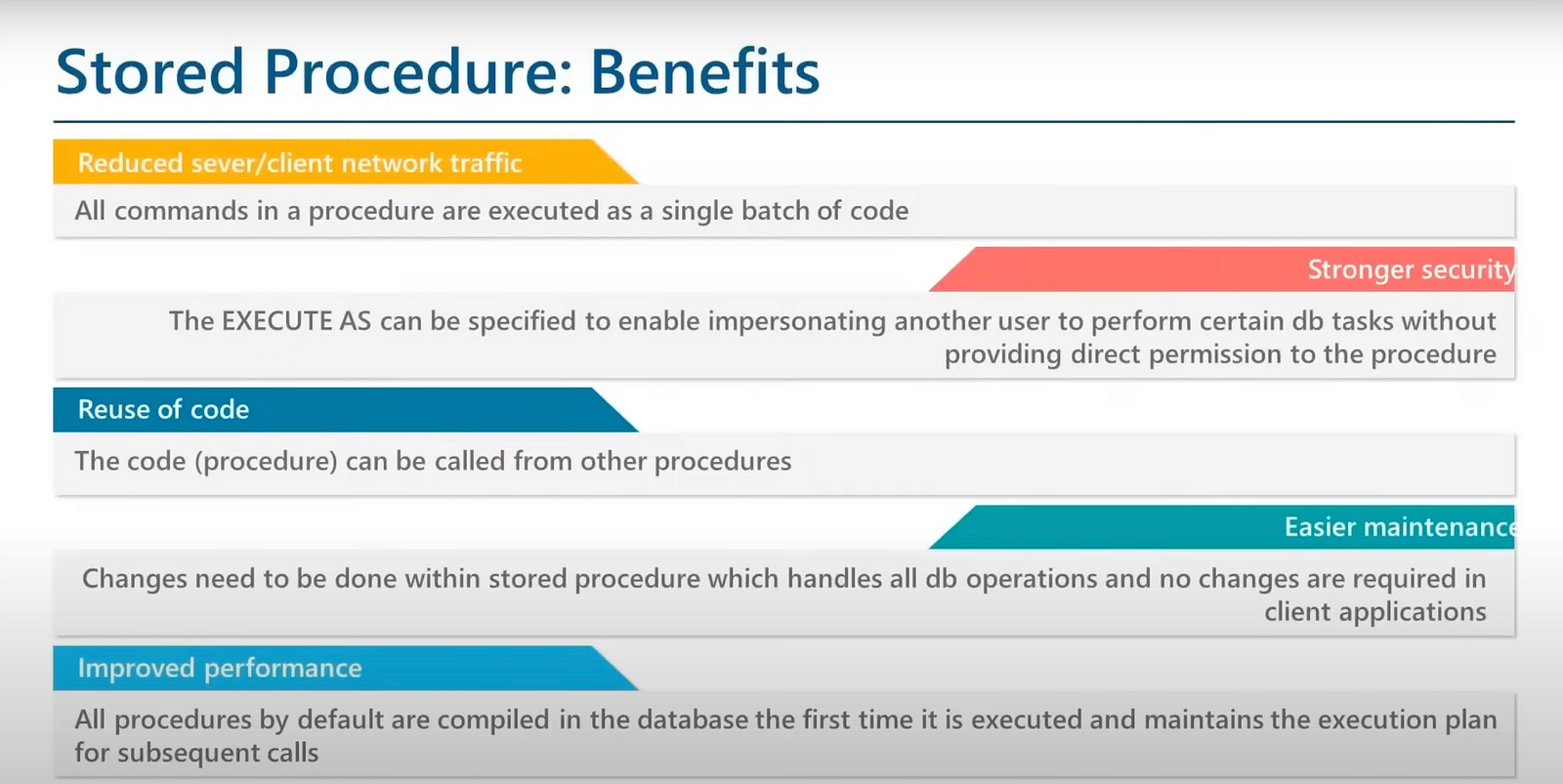
In simple terms, a stored procedure in SQL is like a recipe stored in the database that you can use to perform specific tasks, such as retrieving information or performing calculations, by simply calling its name and providing any necessary inputs. It helps you save time and effort by encapsulating complex operations into reusable chunks of code.
Stored procedures are sets of SQL statements that are stored and executed on the database server. They can accept parameters, perform operations, and return results, providing a way to encapsulate and reuse complex logic within the database.