
HTML forms serve as the gateway for user interaction on the web, enabling users to submit data, provide feedback, and engage with web applications seamlessly. From login pages to contact forms, HTML forms are integral to capturing user input and driving interactive web experiences. In this article, we’ll dive deep into the world of HTML forms, exploring their structure, elements, attributes, and examples to help you harness their full potential in your web development projects.
Understanding HTML Forms:
HTML forms provide a structured way to collect user input, process it on the server side, and deliver a personalized response or perform a specific action. A form typically consists of input fields, checkboxes, radio buttons, dropdown menus, and submit buttons, among other elements, all enclosed within the <form> element.
Syntax:
<form action="submit\_handler.php" method="post">
<!-- Form elements go here -->
</form>
The <form> element requires two essential attributes:
action: Specifies the URL where the form data should be submitted.method: Defines the HTTP method to be used for form submission, typically “get” or “post”.
Example:
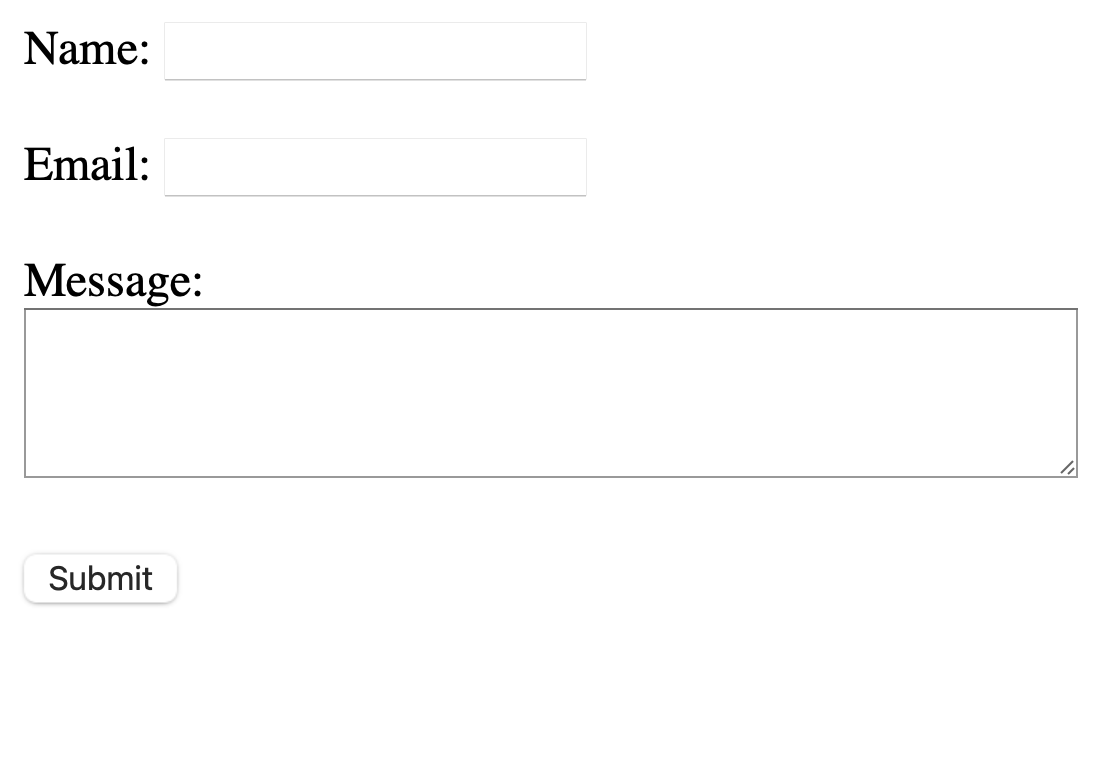
Let’s create a simple contact form with fields for name, email, message, and a submit button:
<form action="submit\_form.php" method="post">
<label for="name">Name:</label>
<input type="text" id="name" name="name"><br><br>
<label for="email">Email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email"><br><br>
<label for="message">Message:</label><br>
<textarea id="message" name="message" rows="4" cols="50"></textarea><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
Result:
Form Elements and Attributes:
HTML forms support various elements and attributes to capture different types of user input and control form behavior:
- Text Input:
<input type="text">- Allows users to enter single-line text. - Email Input:
<input type="email">- Validates input as an email address. - Password Input:
<input type="password">- Masks input characters for password entry. - Textarea:
<textarea>- Allows users to enter multi-line text. - Checkbox:
<input type="checkbox">- Allows users to select one or more options. - Radio Button:
<input type="radio">- Allows users to select a single option from a group. - Dropdown Menu:
<select>- Provides a list of options for users to select from. - Submit Button:
<input type="submit">- Submits the form data to the server. - Reset Button:
<input type="reset">- Resets all form fields to their default values.
Example:
Let’s enhance our contact form by adding checkboxes for user preferences:
<form action="submit\_form.php" method="post">
<label for="name">Name:</label>
<input type="text" id="name" name="name"><br><br>
<label for="email">Email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email"><br><br>
<label for="message">Message:</label><br>
<textarea id="message" name="message" rows="4" cols="50"></textarea><br><br>
<input type="checkbox" id="subscribe" name="subscribe" value="subscribe">
<label for="subscribe">Subscribe to Newsletter</label><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>

With a solid understanding of HTML forms, you can build dynamic and user-friendly web applications that engage and delight users across the digital landscape.